Eyeon:Manual/Fusion 6/3D/Reflections and Refractions
From VFXPedia
[ Main Manual Page ]
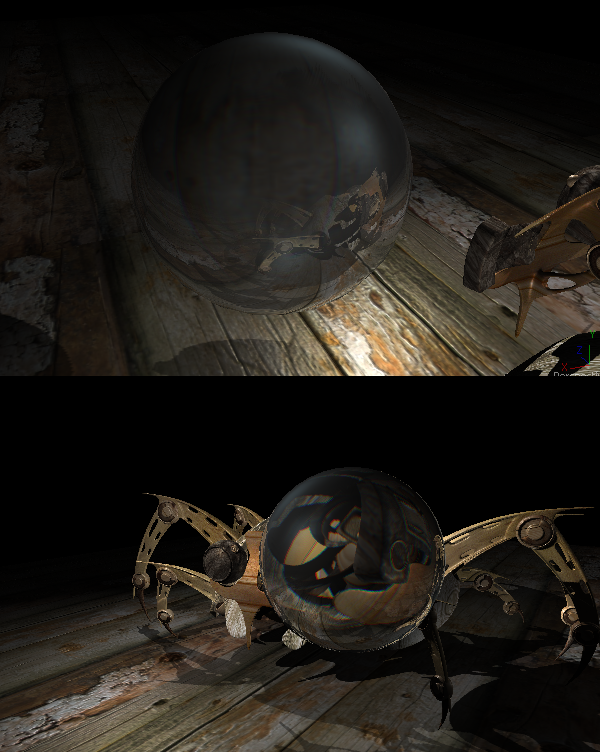
The illumination models in Fusion all support the use of environmental reflection maps created by the Reflect tool in the 3D Material tool category. This tool creates an environmental reflection map which can be used to simulate reflections and refractions on an object. Reflections are direct reflections of the light that hits an object, while refractions simulate the distortion of light seen through semi-translucent surfaces.
The reflections and refractions produced in Fusion are not accurate, raytraced solutions, as these would be much too slow in the context of a compositor. Instead Fusion uses a technique common in games called environment mapping to produce an approximation which is good enough for many scenarios. Environment maps assume an objects environment is infinitely distant from the object and renders it into a cubic or spherical texture surrounding the object.
Fusion 6 provides the Cube Map and Sphere Map tools to help create environment texture maps which will produce more realistic results than a simple flat texture mapped directly to the object.
Environment mapped reflections and refractions do not provide self reflection or any other kind of interaction between different objects. In particular, this infinite distance assumption means that objects can not interact with themselves - eg. the reflections on the handle of a teapot will not show the body of the teapot.. It also means that using objects using the same cubemap will not inter-reflect with each other. For example, two neighboring objects would not reflect each other. A separate cubemap must be rendered for each object.
The Reflect tool outputs a material that can be applied to an object directly, but the material does not contain an illumination model. As a result objects textured directly by the Relfect tool will not respond to lights in the scene. For this reason the Reflect tool is usually combined with the Blinn, Cook Torrance, Phong or Ward tools.
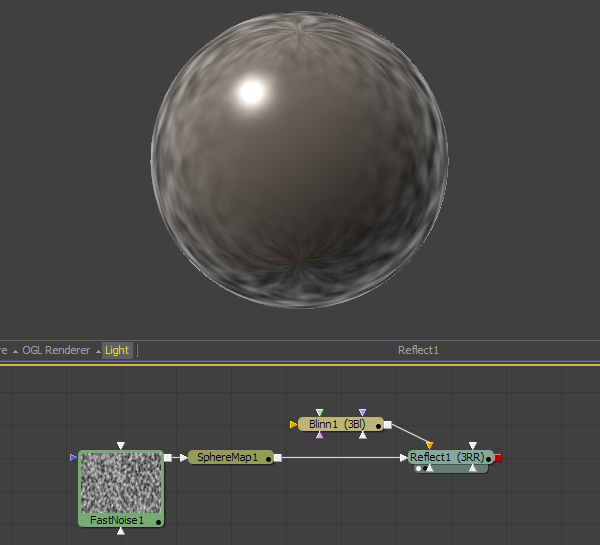
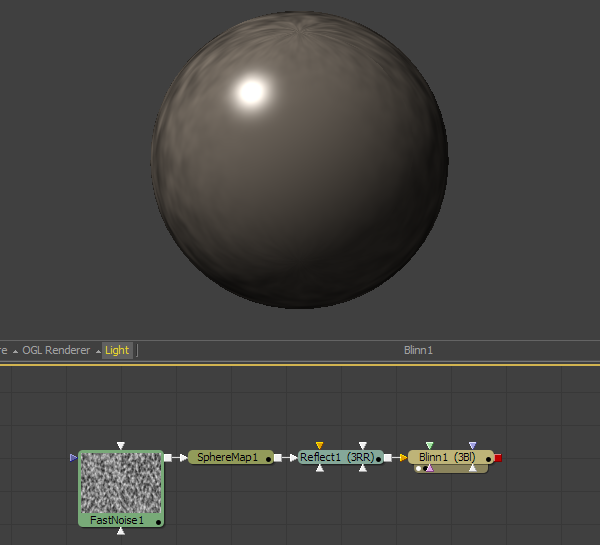
Additionally, reflections and lighting may not interact in a realistic fashion. Environment mapped reflections are a texturing effect that is blended over the background color. That makes it possible to apply the reflection either before or after the lighting model. The images below show different approaches to adding reflections to a material:
In this example the Blinn material is connected to the background material input of the reflection. This causes the Blinn to light the reflection texture.
In this example the Reflection texture is connected to diffuse color component of the Blinn, causing the texture to be multiplied by the diffuse color.
The Channel Boolean Material can be used to provide more control over how these are combined, as discussed in the Eyeon:Manual/Fusion 6/3D/Materials section of this chapter. There is no right approach, experiment and select the approach which provides the appropriate effect.
The Reflect tool calculates the reflection differently depending on what type of tool is connected to its texture inputs. If a tool which produces an environmental texture such as the Sphere Map or Cube Map is connected then the reflection/refraction vectors created by the tool are used to map the texture to the object. Connecting a 2D image or a texture created by the Create Texture tool causes the Reflect tool to use the standard UVW texture coordinates instead.
The reflect tool provides the following texture inputs,
- Reflect.Reflection.Color.Material
- typically receives the environment reflection image
- Reflect.Reflection.Intensity.Material
- typically receives a texture for scaling the constant/by angle strength of the reflection
- Reflect.Refraction.Tint.Material
- Typically receives the refraction environment image.
Refraction only occurs where there is transparency in the background material, which is generally controlled through the Opacity slider and/or the alpha channel of the any material or texture used for the background texture input.
Working with reflection an refraction can be tricky sometimes. Here are some hints to make work easier.
- Keep it subtle. Typically environment mapped reflections use just a hint of reflection, between 0.1 and 0.3 strength. Use higher values only for glossy surfaces like chrome
- Bump maps can add detail to the reflections / refractions. Note that Bump Map also lacks an illumination model, so connect it to the illumination model used by the reflect tool.
- When detailed reflections are not required use a relatively small cubemap, such as 128 x 128 or 256 x 256 pixels, and blur out the reflections.
- In photorealistic renderers the reflection is added to the lighting information of the surface. In Fusion it will blend between the reflection color and the color of the surface. For behaviour closer to the photorealistic renderers, create the reflection separately and add it to the illumination model using a Channel Boolean Material tool.
- The refraction is evaluated only when the ray hits the object. There is no additional computation when the ray would leave the object.
- In practice it can be hard for the human brain to distinguish between a physical correct (ray traced) refraction or an environment refraction - as long as everything looks warped the brain doesn’t notice the precise optics.
- The alpha of refracted pixels is set to 1 even though the pixels are technically transparent.
- If the refraction is not visible even when a texture is connected to Reflect.Refraction.Tint.Material, double check the alpha/opacity values of the background material.
| The contents of this page are copyright by eyeon Software. |