Eyeon:Manual/Fusion 6/Lens Distort
From VFXPedia
[ Main Manual Page ]
Contents |
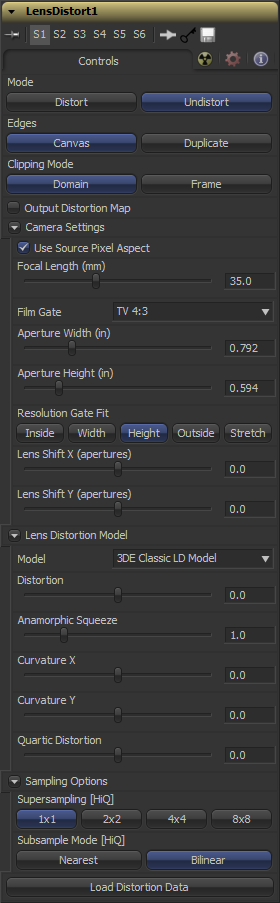
Controls Tab
Undistort removes the lens distortion to create a flattened image. Distort brings the original lens distortion back into the image.
Determines how samples that fall outside of the frame are treated
- Canvas
Pixels outside the frame are set to the default canvas color. In most cases this is black with no alpha.
- Duplicate
Pixels outside the frame are duplicated. This results in “smeared” edges, but is useful when e.g. applying a blur, because black pixels would in that case result in unwanted blurring between the actual image and the black canvas.
- Domain
Retains all pixels that might be moved out of the frame for later re-distoring.
- Frame
Pixels moved outside the frame will be discarded.
Outputs the location of pixels as a warped screen-coordinate map, rather than the actual (un)distorted image.
The options known from the Camera3D are duplicated here. They can either be set manually or connected to an already existing Camera3D.
Select the appropriate 3D equalizer lens distortion model here. 3DE Classic Model, 3DE4 Anamorphic, 3DE4 Radial Fishey or 3DE4 Radial
Please consult the 3D equalizer manual for further explanation. The sliders in the 3DE Classic LD Model are most likely best suited for manually applying (un)distortion,
without having imported lens data.
Sets the number of samples used to determine each destination pixel. As always, higher supersampling leads to higher render times.
1×1 bilinear is usually of sufficient quality, but with high lens distortion near the edges of the lens there will be noticable differences to higher settings.
The type of sample done for each supersample. Nearest will lead to a crisper but more aliased image. Bilinear will give a smoother but also blurrier result.
Allows to load a lens distortion profile, created for example by 3D equalizer.
How to manually determine Lens Distortion
In the ideal world, one would have exact lens-parameters from each lens that was used during the shoot and could use those values to undistort the image.
However, in the real world those parameters have not been taken on set or don’t match.
Another approach is to use a software like e.g. 3DEqualizer which analyzes the footage and delivers a dataset which can be imported into the LensDistort tool right away.
And finally one could try to manually eyeball the amount of lens distortion using the control sliders. To do that one could either look out for horizontal or vertical lines in the footage that are supposed to be straight and straighten them out using the controls, or shoot a full frame checkerboard pattern on set as a reference.
Tips for Lens Distort (edit)
Using the Distortion Map
The distortion map that is produced by this tool contains full pixel coordinates instead of Fusion's usual normalized coordinates (so you should be in float32 mode to start with). To distort an image with it, you need to use the Displace tool. Connect the distortion map to its green foreground input triangle, set the distortion type to XY and put the following expression on both the X and the Y reflection sliders:
1 / Input.Width
This will scale the amount of distortion appropriately so the result looks the same as what the Lens Distort tool would have rendered.
| The contents of this page are copyright by eyeon Software. |