Eyeon:Manual/Fusion 6/Reflect
From VFXPedia
[ Main Manual Page ]
The reflection tool is used to add environment map reflections and refractions to materials. Control is offered over the face on and glancing strength, falloff, per channel refraction indexes and tinting. Several texture map inputs can modify the behaviour of each parameter.
The Reflection tool is usually combined with a standard lighting material such as Blinn, Cook Torrance, Phong or Ward by connecting the output of that tool to the Reflection tools background material input. Then a reflection texture is connected to the reflection texture input. This can be a 2D image, but is more frequently an environmental map created by the SphereMap or CubeMap tools.
Environment mapping is an approximation which assumes that an objects environment is infinitely distant from the object. It's best to picture this as a cube or sphere with the object at the center. In particular, this infinite distance assumption means that objects can not interact with themselves - eg. the reflections on the handle of a teapot will not show the body of the teapot but rather the infinite environment map. It also means that if you use the same cubemap on multiple objects in the scene, those objects will not inter-reflect each other - eg. two neighboring object would not reflect each other. If you want objects to reflect each other you need to render a cubemap for each.
For more information see Reflections and Refractions in this manual.
External Inputs
- Reflect.BackgroundMaterial
- [ orange, optional ] This input expects a 2D image or a 3D material. If a 2D image is provided the tool will treat it as a diffuse texture map applied to a basic material.
- Reflect.Reflection.ReflectionTex
- [ green, optional ] This input expects a 2D image or a 3D material. The RGB channels are used as the reflection texture, and the alpha is ignored.
- Reflect.Reflection.ReflectionIntensityTex
- [ magenta, optional ] This input expects a 2D image or a 3D material. The alpha channel of the texture is multiplied by the intensity of the reflection.
- Reflect.Refraction.RefractionTex
- [ light blue, optional ] This input expects a 2D image or a 3D material. The RGB channels are used as the refraction texture.
- Reflect.BumpmapTex
- [ white, optional ] This input will accept a 2D image or a 3D material then uses the RGB information as texture-space normals.
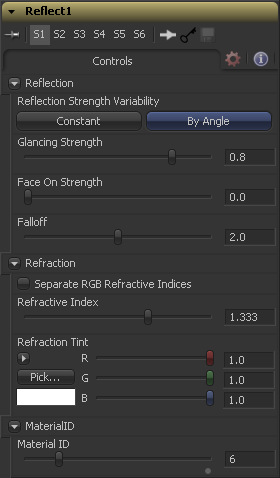
Controls
Reflection
This multibutton control can be set to Constant or By Angle for varying the reflection intensity according to the relative surface orientation to the viewer. The following three controls are only visible when this control is set to By Angle.
[ By Angle ] The Glancing Strength controls the intensity of the reflection for those areas of the geometry where the reflection faces away from the camera.
[ By Angle ] The Face On Strength controls the intensity of the reflection for those parts of the geometry that reflect directly back to the camera.
[ By Angle ] The Falloff controls the sharpness of the transition between the Glancing and Face On Strength regions. It can be considered to be analogous to applying gamma correction to a gradient between the Face On and Glancing values.
[ Constant Angle ]This control is only visible when the reflection strength variability is set to Constant. In this case the intensity of the reflection is constant regardless of the incidence angle of the reflection.
Refraction
If the incoming background material has a lower opacity than 1, then it is possible to use an environment map as refraction texture. So it is possible to simulate refraction effects in transparent objects.
When this checkbox is enabled the Refraction Index slider will be be hidden and three sliders for adjusting the refraction index of the Red, Green and Blue channels will appear in it's place. This allows for simulation of the spectral refraction effects commonly seen in thick imperfect glass, for example.
This slider controls how strongly the environment map will be "deformed" when viewed through a surface. The overall deformation is based on the incidence angle. Since this is a approximation and not a simulation the results are not intended to accurately model real refractions.
The refraction texture is multiplied by the tint color for simulating color filtered refractions. It can be used to simulate the type of coloring found in tinted glass, as seen in many brands of beer bottles, for example.
This slider sets the numeric identifier assigned to this material. This value will be rendered into the MatID auxiliary channel if the according option is enabled in the renderer.
Tips for Reflect (edit)
| The contents of this page are copyright by eyeon Software. |