Settings and Macros/LuminanceControl Description
From VFXPedia
[ Main Manual Page ]
- Other macro tools in this category:
- [ColorFill]
- [InvertColor]
- [InvertedBC]
- [LuminanceControl ]
- [PrimaryGrade]
- [SubtractBGColor]
- [TMI Color]
| LuminanceControl_v01 | Download |
This new macro lets you modify the luminance of the image preserving its saturation.
For example, when you increase the contrast with the BrightnessContrast tool, you also increase the saturation and if you change the gamma, the saturation changes non-linearly in the dark and light areas.
The LuminanceControl macro, however, subtracts the luminance information based on one of three modes: HSV, YUV or HLS (you can choose depending on the situation) and works with it separately from color characteristics.
This can be really important if you have approved colors in the image, but want to change the contrast. It can also help you bring a stylish look to a picture simulating the bleach bypass effect.
Besides, this tool has a wider range for the Low and High controls which enables you not only to increase the contrast, but also to decrease it.
Node Inputs
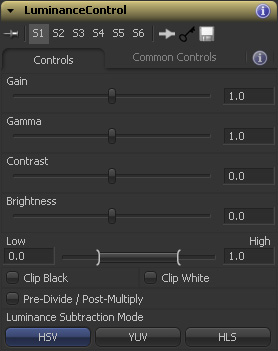
Controls Tab
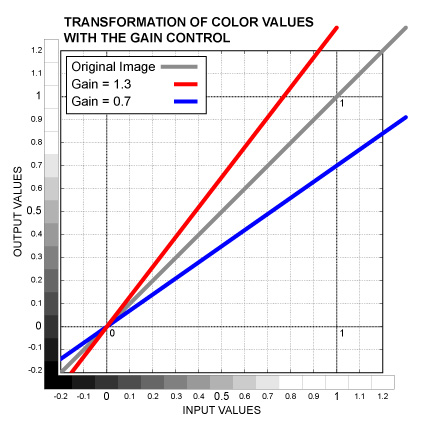
Slider control. Increases the image brightness by multiplying the color values by the control value. Acts similarly to the Contrast control, but affects brighter pixels more, preserving the black point. See the graph below.
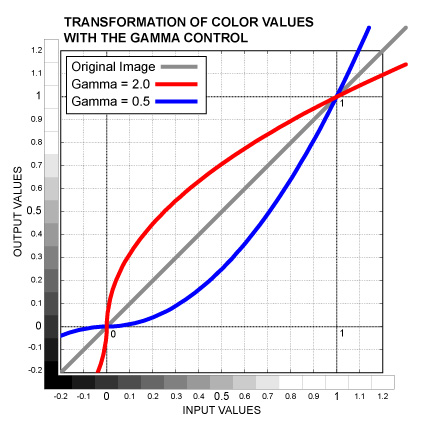
Slider control. Adjusts color values between the Black Point and White Point, leaving the Black Point and White Point intact. Outside the Black to White range colors are affected in the opposite direction. Mathematically, it's exponentiation, color values are raised to the power of one divided by the control value. See the graph below.
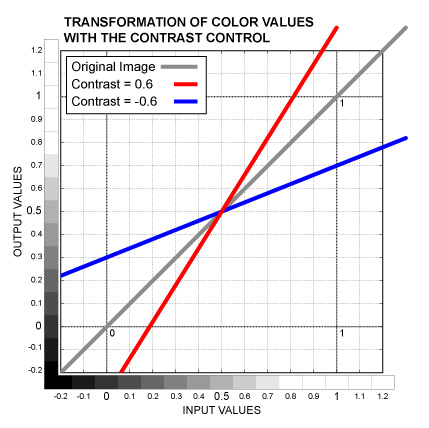
Slider control. Increases the contrast of the image. The operation is similar to the Gain, but it shifts the black and white points to the opposite directions, preserving the mid-gray. See the graph below.
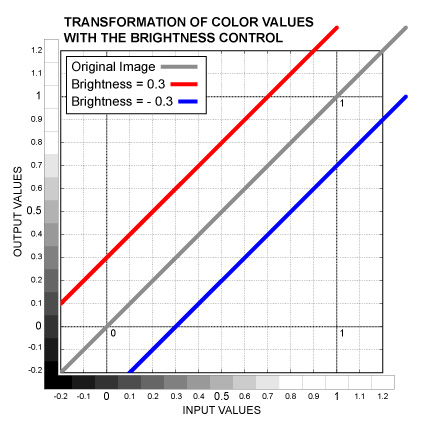
Slider control. Increases or decreases all the luminance values equally shifting the Black Point, Mid-gray and White Point to the same direction by the same amount. The control value is added to the color values. This operation is also known as Offset or Pedestal. See the graph below.
Range control. Similar to Input Levels control. Low defines what luminance value should become black (the opposite to Lift). High defines what luminance value should become white (the opposite to Gain). When you move the ends of the range closer, you increase the contrast and when you move them further from each other, you decrese the contrast.
Checkbox control. Clips the luminance values below 0 (darker than black).
Checkbox control. Clips the luminance values above 1 (brighter than white).
Checkbox control. Preserves the the opacity of transparent areas affecting the colors proportionally to the Alpha values.
Processing Examples
Development History and Discussion on PigsFly
www.compositing.tv