Settings and Macros/PrimaryGrade Description
From VFXPedia
[ Main Manual Page ]
- Other macro tools in this category:
- [ColorFill]
- [InvertColor]
- [InvertedBC]
- [LuminanceControl ]
- [PrimaryGrade]
- [SubtractBGColor]
- [TMI Color]
| PrimaryGrade_v06-6 | Download |
Allows you to set the Black and White point of an image simply by picking the colors from a reference or by using color wheels. Additional color wheels control Brightness and Gamma. There are also controls for Saturation, color range clipping and options allowing to work comfortably in linear space.
A big advantage of the PrimaryGrade compared to the ColorCorrector tool is all the controls for the Red, Green and Blue channels are exposed on one page in a compact form. You can quickly access them and adjust colors simultaneously by using either sliders or color wheels instead of digging in numerous subcategories. It also means that you can easily work out at a glance, what color adjustments are performed by a particular PrimaryGrade in the Flow.
To access the color wheels, press the triangle button next to RGB sliders.
The macro has separate tabs for the Shadows/Midtones/Highlights ranges though to let you isolate adjustable colors based on the luminance if needed.
External Inputs
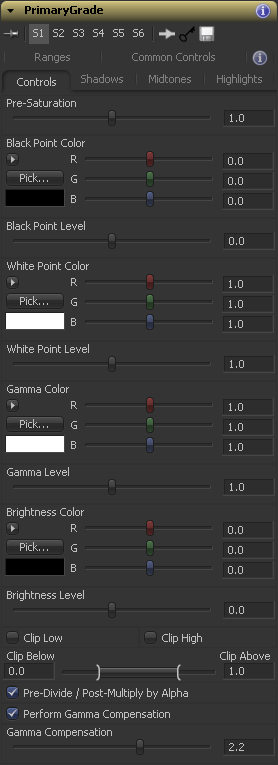
Controls Tab
Slider control. Adjusts the color saturation of the source image. Pre-Saturation is performed before all the other operations, so if you tint the image using other controls, tinting will persist even if the Pre-Saturation is set to 0.
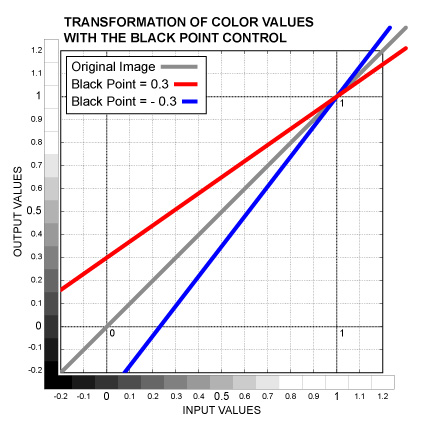
Color control. Sets the Black Point for separate channels. Color values are scaled (multiplied by the control value) so that the White Point remains the same. Dark colors are affected the most, however, colors which are brighter than the White Point value are affected in the opposite direction. This operation is sometimes called the Lift. See the graph below.
Slider control. The same as the Black Point Color, but affects all the three channels equally.
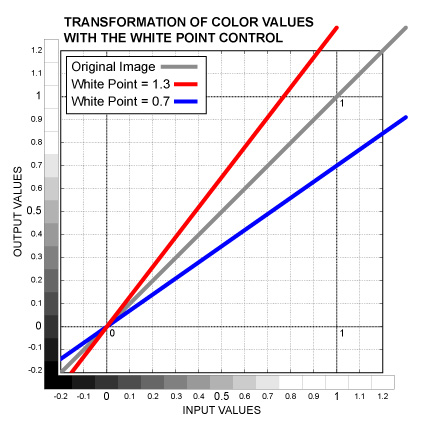
Color control. Sets the White Point for separate channels. Color values are scaled (multiplied by the control value) so that the Black Point remains the same. Bright colors are affected the most, however, colors which are darker than the Black Point value are affected in the opposite direction. This operation is similar to Gain. See the graph below.
Slider control. The same as the White Point Color, but affects all the three channels equally.
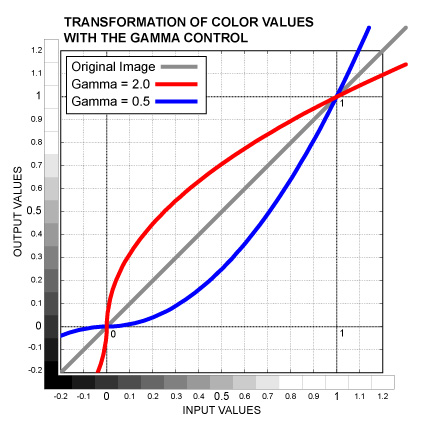
Color control. Adjusts color values between the Black Point and White Point, leaving the Black Point and White Point intact. Outside the Black to White range colors are affected in the opposite direction. Mathematically, it's exponentiation, color values are raised to the power of one divided by the control value. See the graph below.
Slider control. The same as the Gamma Color, but affects all the three channels equally.
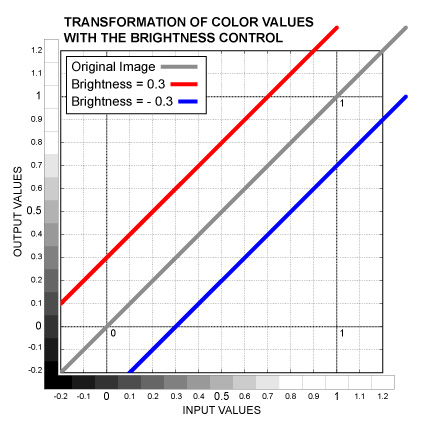
Color control. Increases or decreases color values in the whole color range for separate channels. The Black Point and White Point are affected equally as well as everything in between. The control value is added to the color values. This operation is also known as Offset or Pedestal. See the graph below.
Slider control. The same as the Brightness Color, but affects all the three channels equally.
Checkbox control. Clips all the color values below the range defined by the Clip Below / Clip Above control.
Checkbox control. Clips all the color values above the range defined by the Clip Below / Clip Above control.
Range control. Defines the range for color clipping.
Checkbox control. Preserves the the opacity of transparent areas.
Checkbox control. Useful if you work with a display LUT which performs gamma correction. It adjusts the gamma internally so that the colors you work with in the PrimaryGrade correspond to the colors you see in the Display View.
Slider control. The amount of Gamma Compensation should be equal to the gamma correction of your LUT.
Processing Examples
Download PrimaryGrade_v06-3 (for Fusion 6.2 and below)
Development History and Discussion on PigsFly
www.compositing.tv