Eyeon:Manual/Fusion 6/Color Matrix
From VFXPedia
[ Main Manual Page ]
The ColorMatrix allows for a vast number of operations to modify values individually in the different color channels.
Controls
- Update Lock
- When this control is selected, Fusion will not render the tool. This is useful for setting up each value of the tool, then turning Update Lock off in order to render it.
This defines what type of operations actually take place. The horizontal rows define the output values of the tool, the vertical columns the input values. The „add“ column allows for simple adding of values to the individual color channels.
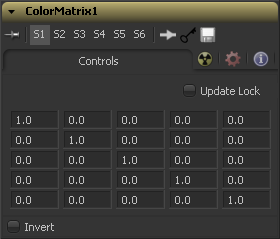
By default the output values are identical to the input values.
100% of the Red channel input is copied to the Red channel output. 100% of the Green channel input is copied to the Green channel output. 100% of the Blue channel input is copied to the Blue channel output. 100% of the Alpha channel input is copied to the Alpha channel output.
We can also write the default settings as mathematical equations
- [R out] = 1 * [R in] + 0 * [G in] + 0 * [B in] + 0 * [A in] + 0
- [G out] = 0 * [R in] + 1 * [G in] + 0 * [B in] + 0 * [A in] + 0
- [B out] = 0 * [R in] + 0 * [G in] + 1 * [B in] + 0 * [A in] + 0
- [A out] = 0 * [R in] + 0 * [G in] + 0 * [B in] + 1 * [A in] + 0
Enabling this option will invert the Matrix. Think of swapping channels around, doing other operations with different tools and then copy and paste the original ColorMatrix and set it to invert to get your channels back to the original.
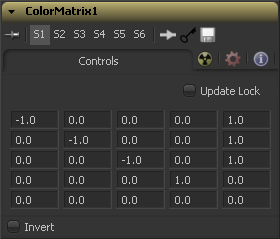
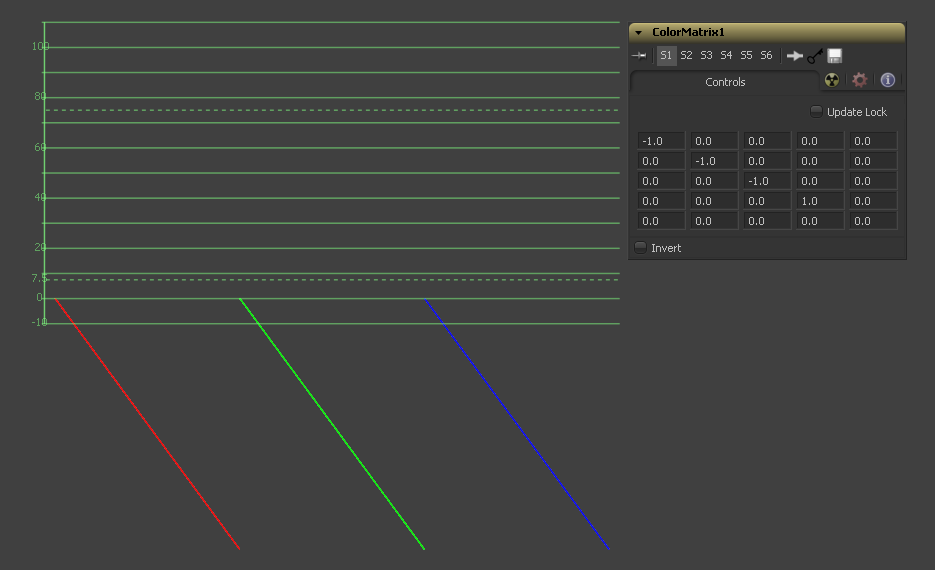
Example 1 - Invert
If we want to do a simple invert or negative of the color values,
but keep our alpha channel as it is, the matrix would look like this
Observe the fact that we have to Add 1 to each channel to push the inverted values back into the positive numbers.
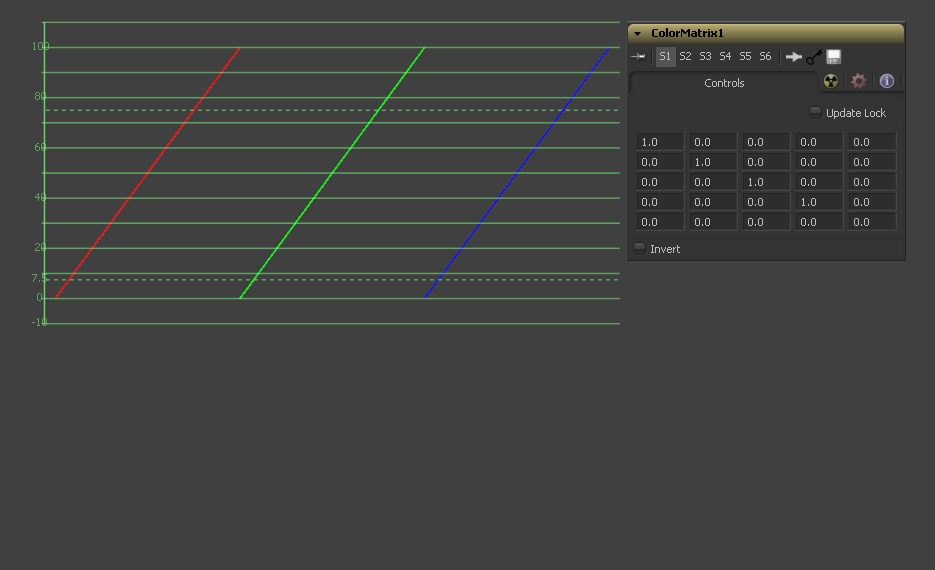
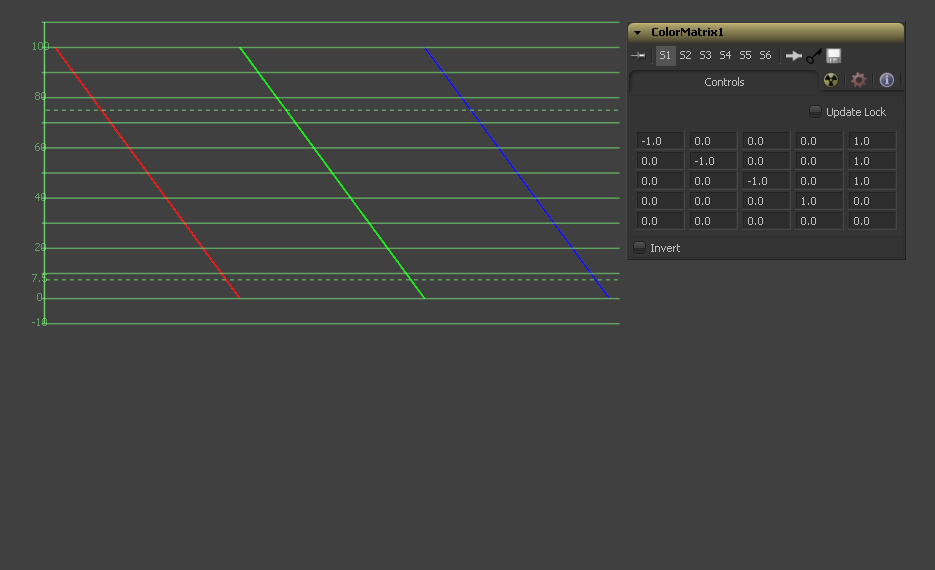
Let's follow this example step by step by viewing the waveform of a 32bit grayscale gradient
Example 2 - Brightness per Channel
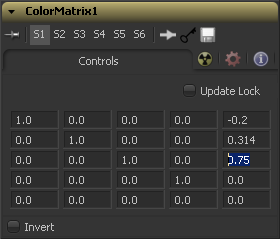
Let's influence the brightness of each channel individually
This subtracts 0.2 from the Red channel, adds 0.314 to the Green channel and adds 0.75 to the Blue channel whilst keeping Alpha as it is.
Example 3 - Copying values
Of course we can also copy color values back and forth between individual channels.
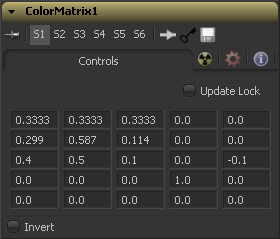
Let's make the Red channel contain the luminance values of the image based on thirds
and the Green channel contain the luminance values based on the proper black-and-white conversion method, whereas in the Blue channel we use a third method based on getting more information from Red and less from Blue.
We also lower the Blue channel's brightness by 0.1
and replace the Alpha Channel with the original Blue channel.
You see that this tool is immensely versatile for all sorts of mathematical channel-based operations.