Eyeon:Manual/Fusion 6/Custom Filter
From VFXPedia
[ Main Manual Page ]
- Create Bumpmap
- Custom Filter
- Erode / Dilate
- Filter
- Rank Filter
Contents |
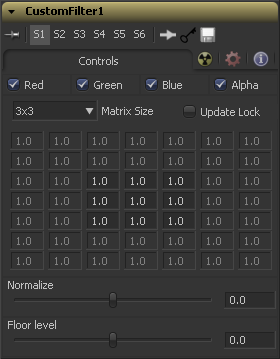
A kernel filter is an array (or grid) of either 3 x 3, 5 x 5 or 7 x 7 values. The center of the array represents the current pixel, and entries nearby represent adjacent pixels. A value of 1 applies the full value of the pixel to the filter. A value of 0 ignores the pixel's value. A value greater than one multiplies the pixel's affect on the result. Negative values can also be entered, where the value of the pixel will be subtracted from the average. Only integer values can be entered, 0.5 is not valid.
Controls
The color corrector defaults to operating on R, G, B and A channels. Selective channel editing is possible by clicking the checkboxes beside each channel, making selected channels active or inactive.
This is not the same as the RGBA checkboxes found under the common controls. The tool takes these controls into account before it processes. Deselecting a channel will cause the tool to skip that channel when processing, speeding up the rendering of the effect. In contrast, these controls under the common controls tab are applied after the tool has processed.
Use this drop-down to set the size of the filter at 3 x 3 pixels, 5 x 5 pixels or 7 x 7 pixels, thus setting the radius of the pixels sampled. The larger the size, the more time it takes to render.
- Update Lock
- When this control is selected, Fusion will not render the tool. This is useful for setting up each value of the tool, then turning Update Lock off in order to render it.
The Filter Matrix control is a 7 x 7 grid of text boxes where a number is entered to represent how much influence each pixel has on the overall convolution filter. The text box in the center represents the pixel that is processed by the filter. The text box to the left of the center represents the pixel to the immediate left, and so forth.
.The default Matrix size is 3 x 3. Only the pixels immediately adjacent to the current pixel will be analysed. If a larger Matrix size is set, more of the text boxes in the grid will be enabled for input.
This controls the amount of filter normalization that is applied to the result. Zero will give a normalized image. Positive values will brighten or raise the level of the filter result. Negative values will darken or lower the level.
This will add or subtract a minimum, or Floor Level, to the result of the filtered image. Zero will not add anything to the image. Positive values will add to the filtered image and Negative values will subtract from the image.
Examples
0 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 0

will have zero effect from its neighboring pixels and the resulting image would be unchanged.
}}
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1 1

...where the neighboring pixels are averaged with the center, resulting in a softening effect.
-5 0 0
0 1 0
0 0 5
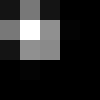
If parts of the image that is processed are very smooth in color, the neighboring values will be very similar. In parts of the image where the pixels are different (i.e. an edge), the results will be different and tend to highlight or emboss edges in the image.
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 1 1

...and sliding Normalize to Positive will make the image go brighter or glow, simulating film over-exposure.
-1 0 0
0 0 0
0 0 1
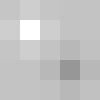
...and sliding Floor Level to Positive will look like a relief filter.
Tips for Custom Filter (edit)
EyeonTips:Manual/Fusion 6/Custom Filter
| The contents of this page are copyright by eyeon Software. |