< Previous | Contents | Next >
the clips to HD. The full resolution of the individual 4K clips is not available in Fusion and is therefore handed off to the Color page at the rescaled size. To maintain the full resolution of source clips, bring only one clip into the Fusion page from the Edit or Cut page Timeline, and then bring other clips into the Fusion composition using the Media Pool. Of course, if your clips are full HD and your timeline is full HD, then creating a Fusion clip or compound clip does not affect the resolution.
Color Bit Depths
The term bit depth describes how many colors are available in the color palette used to make up an image. The higher the bit depth, the greater the precision of color in the image, and therefore the greater the color reproduction. The higher precision is most apparent in gradients with subtle changes. Lower bit-depth gradients have noticeable banding artifacts, whereas higher bit-depth images can reproduce more colors, so fewer, if any, banding artifacts occur. The Fusion page within DaVinci Resolve always uses 32-bit float bits per channel precision to process images. However, in Fusion Studio you can choose to process images with 8-bit integer, 16-bit integer, 16-bit float, and 32-bit float bits per channel. Although always working at 16-bit float or 32-bit float will produce the best quality, it may be more efficient to use a lower bit depth if your images are 8-bit or 16-bit integer formats to begin with.
Understanding Integer vs. Float
Generally, 8-bit integer color processing is the lowest bit depth you’ll come across for video formats. 8-bit images come from older or consumer-grade video equipment like mobile phones and
camcorders. If you try to perform any significant gamma or color correction on 8-bit images, you can often see more visible banding.
![]()
16-bit integer color depth doubles the amount of precision, eliminating problems with banding. Although you can select 16-bit integer processing for an 8-bit clip, it does not reduce banding that already exists in the original file. Still, it can help when adding additional effects to the clip. This sounds like the best solution until you realize that many digital cameras like Blackmagic Design URSA Mini Pro and others record in formats that can capture over-range values with shadow areas below 0.0 and super highlights above 1.0, which are truncated in 16-bit integer.
The 16-bit float color depth sacrifices a small amount of the precision from standard 16-bit integer color depth to allow storage of color values less than 0 and greater than 1.0. 16-bit float, sometimes called half-float, is most often found in the OpenEXR format and contains more than enough dynamic range for most film and HDR television purposes yet requires significantly less memory and processing time than is required for full float, 32-bit images.
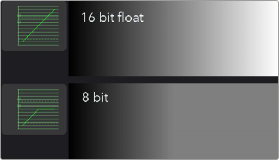
Preserving over-range values allows you to change exposure while maintaining highlights