< Previous | Contents | Next >
Attaching Masks to an Image for Rotoscoping
There are two ways you’ll typically attach a Mask node, such as a Polygon node, so that it adds an alpha channel to an image for compositing later in the node tree.
Using a MatteControl Node
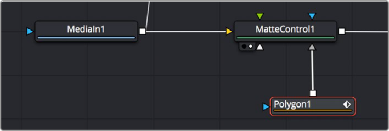
The MatteControl node is the main node used for combining masks in different ways and inserting the result into an image stream. The MatteControl node is attached downstream of the node outputting the image you want to rotoscope. You’ll typically attach a Polygon or B-Spline node to the Garbage Matte input of the MatteControl node to use the spline as an alpha channel.

Feeding a Polygon node to a MatteControl node to perform rotoscoping
To use this setup, you’ll load the MatteControl node into the viewer and select the Polygon node to expose its controls so you can draw and modify a spline while viewing the image you’re rotoscoping. The MatteControl node’s Garbage Matte > Invert checkbox lets you choose which part of the image becomes transparent.
Connecting a Mask to a MediaIn or Loader Node’s Input
![]()
This method is a bit simpler but requires you to know that you can view one node while adjusting another node, even if that other node is disconnected. If you add an unattached Mask node such as a Polygon or B-Spline node, and then place a MediaIn or Loader node directly into the viewer while selecting the Mask node, you can draw a spline to rotoscope the image.
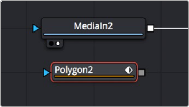
Rotoscoping a MediaIn node using a disconnected Polygon node
When you’re finished rotoscoping, you simply connect the Polygon node’s output to the Loader node’s input, and an alpha channel is automatically added to that node.
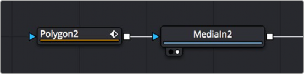
Connecting a Polygon node to a MediaIn node to use a spline as an alpha channel

TIP: If you connect a Mask node to a MediaIn or Loader node’s effect input without any shapes drawn, that mask outputs full transparency, so the immediate result is that the image output by the MediaIn or Loader node becomes completely blank. This is why when you want to rotoscope by connecting a mask to the input of a MediaIn or Loader node, you need to work within a disconnected Mask node first. Once the shape you’re drawing has been closed, connect the Mask node to the MediaIn or Loader’s input, and you’re good to go.
TIP: If you connect a Mask node to a MediaIn or Loader node’s effect input without any shapes drawn, that mask outputs full transparency, so the immediate result is that the image output by the MediaIn or Loader node becomes completely blank. This is why when you want to rotoscope by connecting a mask to the input of a MediaIn or Loader node, you need to work within a disconnected Mask node first. Once the shape you’re drawing has been closed, connect the Mask node to the MediaIn or Loader’s input, and you’re good to go.
TIP: If you connect a Mask node to a MediaIn or Loader node’s effect input without any shapes drawn, that mask outputs full transparency, so the immediate result is that the image output by the MediaIn or Loader node becomes completely blank. This is why when you want to rotoscope by connecting a mask to the input of a MediaIn or Loader node, you need to work within a disconnected Mask node first. Once the shape you’re drawing has been closed, connect the Mask node to the MediaIn or Loader’s input, and you’re good to go.