< Previous | Contents | Next >
Garbage mattes are mask nodes or images connected to the garbage matte input on the node.
The garbage matte is applied directly to the alpha channel of the image. Generally, garbage mattes are used to remove unwanted elements that cannot be keyed, such as microphones and booms. They are also used to fill in areas that contain the color being keyed but that you wish to maintain.
Garbage mattes of different modes cannot be mixed within a single tool. A Matte Control node is often used after a Keyer node to add a garbage matte with the opposite effect of the matte applied to the keyer.
Enabling Invert will invert the garbage matte, before it is combined with the source alpha.
Select this option to cause the keyer to multiply the color channels of the image against the alpha channel it creates for the image. This option is usually enabled and is on by default.
Deselect this checkbox and the image can no longer be considered premultiplied for purposes of merging it with other images. Use the Subtractive option of the Merge node instead of the Additive option.
For more information on these Merge node settings, see Chapter 35, “Composite Nodes,” in the Fusion Reference Manual.
Common Controls Settings Tab
The Settings tab in the Inspector is also duplicated in other matte nodes. These common controls are described in detail at the end of this chapter in “The Common Controls” section.
![]()
Clean Plate
The Clean Plate node
Clean Plate Node Introduction
The Clean Plate tool is a pre-keying node used to generate an image of the green or blue color screen to smooth out the lighting differences. The output of the Clean Plate is later connected to the Clean Plate input on the Delta Keyer so it can key fine detail without choking or clipping the matte.
How to Create a Clean Plate
Creating a clean plate is the opposite of creating a key. When keying, you try to remove the green or blue color. When creating a clean plate, you try to keep as much of the blue- or green-screen as possible. By box selecting areas of the screen color in the viewer, you end up with an image of the green/blue screen. A transparent cutout represents everything that is not part of the blue or green screen.

Once you have the selection, the Erode control expands the pre-matte, removing any small pixels of non-green/blue screen around the edges. Then, growing the pre-matte fills in the holes until you have a solid blue or green image.
Inputs
The Clean Plate node includes three inputs in the Node Editor.
— Input: The orange input accepts a 2D image that contains the green or blue screen.
— Garbage Matte: The white garbage matte input accepts a mask shape created by polylines, basic primitive shapes, paint strokes, or bitmaps masks. Connecting a mask to this input causes areas of the image that fall within the matte to be excluded from the clean plate. For a clean plate, garbage mattes should contain areas that are not part of the blue or green screen.
— Effect Mask: The optional blue input expects a mask shape created by polylines, basic primitive shapes, paint strokes, or bitmaps masks. Connecting a mask to this input limits the pixels where the clean plate is generated. An effects mask is applied to the tool after the tool is processed.
![]()
Basic Node Setup
The Clean Plate node and the Delta Keyer are two separate branches stemming from the main image you want to key. The green-screen or blue-screen clip is breached to connect to both the orange image input on the Clean Plate and the orange image input on the Delta Keyer. The output of the clean plate is then connected to the magenta clean plate input on the Delta Keyer. The output of the Delta Keyer is then used as the foreground to a Merge.
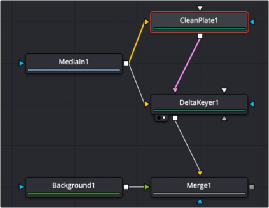
A Clean Plate connected to a Delta Keyer
Inspector
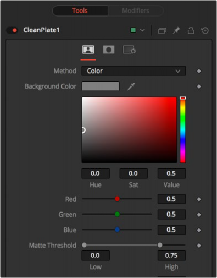
The Clean Plate tab
Plate Tab
The Plate tab contains the primary tools for creating a clean plate. Using this tab, you drag over the areas in the viewer, and then use the Erode and Grow Edges sliders to create the clean plate.
The Method menu selects the type of color selection you use when sampling colors in the viewer.
— Color: Color uses a difference method to separate the background color. This works well on screen colors that are even.
![]()
— Ranges: Ranges uses a chroma range method to separate the background color. This is a better option for shadowed screen or screens that have different colors.
This range slider sets the lower threshold using the handle on the left and sets the upper threshold using the handle on the right.
Any value below the lower threshold becomes black or transparent in the matte.
Any value above the upper threshold becomes white or opaque in the matte. All values within the range maintain their relative transparency values. This control is often used to reject salt and pepper noise in the matte.
The Erode slider decreases the size of the screen area. It is used to eat away at small non-screen color pixels that may interfere with creating a smooth green- or blue-screen clean plate.
Crop trims in from the edges of the image.