< Previous | Contents | Next >
Similar to lights, the default 3D Viewer has shadows turned off. To see shadows cast from the lighting you’ve created, you must turn them on.
— Right-click within the 3D Viewer and choose 3D Options > Shadows from the contextual menu. Enabling shadows will automatically turn on lighting, if it is not already turned on.

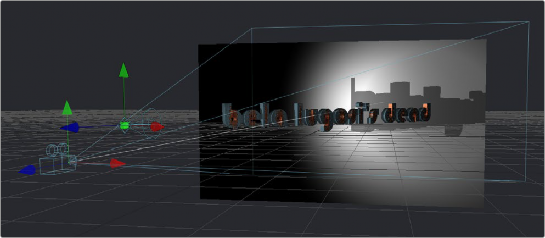
A 3D scene with shadows enabled along with the lights

NOTE: The shadows shown in the 3D Viewer are always hard edged. Soft shadows are available for output to the rest of your composition in the software renderer of the Renderer3D node.
NOTE: The shadows shown in the 3D Viewer are always hard edged. Soft shadows are available for output to the rest of your composition in the software renderer of the Renderer3D node.
NOTE: The shadows shown in the 3D Viewer are always hard edged. Soft shadows are available for output to the rest of your composition in the software renderer of the Renderer3D node.
![]()
Transparency in 3D Viewers
Image planes and 3D objects are obscured by other objects in a scene depending on the X, Y, and Z position coordinates of each object in 3D space. The default method used to determine which polygons are hidden and which are shown based on these coordinates is called Z-buffering.
Z-buffering is extremely fast but not always accurate when dealing with multiple transparent layers in a scene. Fortunately, there is another option for more complex 3D scenes with transparency: Sorted. The Sorted method can be significantly slower in some scenes but will provide more accurate results no matter how many layers of transparency happen to be in a scene.
The default behavior in the viewer is to use Z-buffering, but if your scene requires the Sorted method, you can easily change this.
— Right-click anywhere within the 3D Viewer and choose one of the options in the Transparency submenu of the contextual menu;
— Full Sort: Renders every polygon in Z order to produce the most accurate rendering of transparency.
— Quick Sort: Reorders the polygons in the scene serially, from back to front, to produce a reasonably accurate rendering of transparency.