< Previous | Contents | Next >

The Soft Clip node
Soft Clip Node Introduction
The Soft Clip node is used to fade out geometry and particles that get close to the camera. This helps avoid the visible “popping off” that affects many particle systems and 3D flythroughs.
This node is very similar to the Fog 3D node, in that it is dependent on the geometry’s distance from the camera.
Inputs
The Soft Clip includes only a single input for a 3D scene that includes a camera connected to it.
![]()
— SceneInput: The orange scene input is a required connection. It accepts a 3D scene input that includes a Camera 3D node.
Basic Node Setup
The Soft Clip node is usually placed just before the Renderer 3D node to ensure that downstream adjustments to lighting and textures do not affect the result. It can be placed in any part of the 3D portion of the node tree if the soft clipping effect is only required for a portion of the scene.
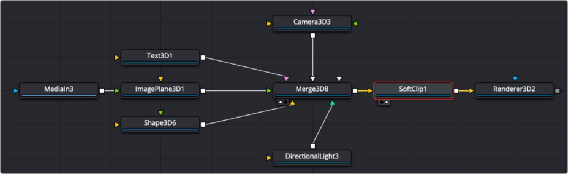
Soft Clip placed between a Merge 3D and a Renderer 3D node
Inspector
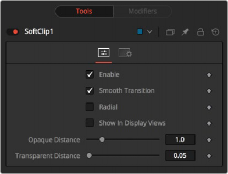
Soft Clip controls
Controls Tab
The Controls tab determines how an object transitions between opaque and transparent as it moves closer to the camera.
This checkbox can be used to enable or disable the node. This is not the same as the red switch in the upper-left corner of the Inspector. The red switch disables the tool altogether and passes the image on without any modification. The Enable checkbox is limited to the effect of the tool. Other parts, like scripts in the Settings tab, still process as normal.
By default, an object coming closer and closer to the camera slowly fades out with a linear progression. With the Smooth Transition checkbox enabled, the transition changes to a nonlinear curve, arguably a more natural-looking transition.
![]()
By default, the soft clipping is done based on the perpendicular distance to a plane (parallel with the near plane) passing through the eye point. When the Radial option is checked, the Radial distance to the eye point is used instead of the Perpendicular distance. The problem with Perpendicular distance soft clipping is that when you move the camera about, as objects on the left or right side of the frustum move into the center, they become less clipped, although they remain the same distance from the eye. Radial soft clip fixes this. Sometimes Radial soft clipping is not desirable.
For example, if you apply soft clip to an object that is close to the camera, like an image plane, the center of the image plane could be unclipped while the edges could be fully clipped because they are farther from the eye point.
Normally, the effect is only visible when the scene is viewed using a Camera node. When enabled, the soft clip becomes visible in the scene from all points of view.
Defines the range of the soft clip. The objects begin to fade in from an opacity of 0 at the Transparent distance and are fully visible at the Opaque distance. All units are expressed as distance from the camera along the Z-axis.