< Previous | Contents | Next >
A text modifier is used to output Time Code for the current frame. See “Text Modifiers” at the end of this chapter.
Use this option to connect the text generated by this Text node to the published output of another node.
Transform 3D [3Xf]

The Transform 3D node
Transform 3D Node Introduction
The Transform 3D node can be used to translate, rotate, or scale all the elements within a scene without requiring a Merge 3D node. This can be useful for hierarchical transformations or for offsetting objects that are merged into a scene multiple times. Its controls are identical to those found in other 3D nodes’ Transformation tabs.
Inputs
![]()
The Transform node has a single required input for a 3D scene or 3D object.
— Scene Input: The orange scene input is connected to a 3D scene or 3D object to apply a second set of transformation controls.
Basic Node Setup
The Transform 3D node adds 3D position, rotation, and pivot control onto any existing transforms in the 3D node prior to it. You can combine multiple Transform 3D nodes together to build parenting or hierarchical movement.
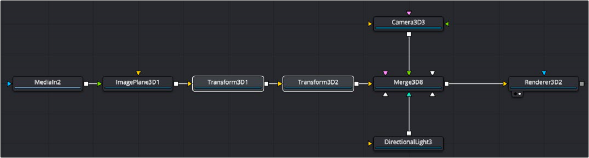
Transform 3D nodes strung together to create a parenting hierarchy
Inspector
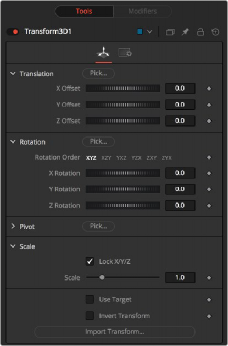
Transform 3D controls
Controls Tab
The Controls tab is the primary tab for the Transform 3D node. It includes controls to translate, rotate, or scale all elements within a scene without requiring a Merge 3D node.
![]()
— X, Y, Z Offset: Controls are used to position the 3D element in 3D space.
— Rotation Order: Use these buttons to select the order used to apply the rotation along each axis of the object. For example, XYZ would apply the rotation to the X-axis first, followed by the Y-axis, and then the Z-axis.
— X, Y, Z Rotation: Use these controls to rotate the object around its pivot point. If the Use Target checkbox is selected, then the rotation is relative to the position of the target; otherwise, the global axis is used.
— X, Y, Z Pivot: A pivot point is the point around which an object rotates. Normally, an object rotates around its own center, which is considered to be a pivot of 0,0,0. These controls can be used to offset the pivot from the center.
— X, Y, Z Scale: If the Lock X/Y/Z checkbox is checked, a single scale slider is shown. This adjusts the overall size of the object. If the Lock checkbox is unchecked, individual X, Y, and Z sliders are displayed to allow scaling in any dimension.

NOTE: If the Lock checkbox is checked, scaling of individual dimensions is not possible, even when dragging specific axes of the Transformation widget in Scale mode.
NOTE: If the Lock checkbox is checked, scaling of individual dimensions is not possible, even when dragging specific axes of the Transformation widget in Scale mode.
NOTE: If the Lock checkbox is checked, scaling of individual dimensions is not possible, even when dragging specific axes of the Transformation widget in Scale mode.
Selecting the Use Target checkbox enables a set of controls for positioning an XYZ target. When Use Target is enabled, the object always rotates to face the target. The rotation of the object becomes relative to the target.
Opens a file browser where you can select a scene file saved or exported by your 3D application. It supports the following file types:
LightWave Scene | .lws |
Max Scene | .ase |
Maya Ascii Scene | .ma |
dotXSI | .xsi |
![]()
The Import Transform button imports only transformation data. For 3D geometry, lights and cameras, consider using the File > FBX Import option from the menus.
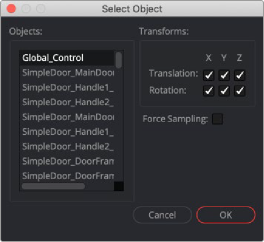
Import Transform Browser
Onscreen Transformation controls provide an alternative way of using the controls in the Inspector. The viewer includes modes for transformation, rotation, and scaling. To change the mode of the onscreen controls, select one of the three buttons in the toolbar along the side of the viewer.
The modes can also be toggled using the keyboard shortcut Q for translation, W for rotation, and E for scaling. In all three modes, an individual axis of the control may be dragged to affect just that axis, or the center of the control may be dragged to affect all three axes.