< Previous | Contents | Next >
— Autosnap Points: When moving points in the Keyframes Editor, the points will snap to the fields or to the frames, or they can be moved freely.
— Guides: When moving points in the Keyframes Editor, the point will snap to the guides that are placed in the Timeline graph.
— Autosnap Guides: When moving or creating guides, the guides will snap to the fields or to the frames, or they can be moved freely.
— Autoscale: Keeps the Timeline scales intact while changing the editable spline content in the graph. When set to scroll, the Timeline scrolls horizontally and vertically to show all or most of the spline points when changing the editable spline content in the graph. When set to Fit, the Timeline zooms to fit all points within the graph, if necessary.
— Tools Display Mode: This menu controls the default sort order of the tools displayed in the Keyframes Editor. The default can be changed using the Sort order menu in the upper right of the Keyframes Editor.
Tweaks
![]()
The Tweaks preferences handle a collection of settings for fine-tuning Network rendering in Fusion Studio and graphics hardware behavior.
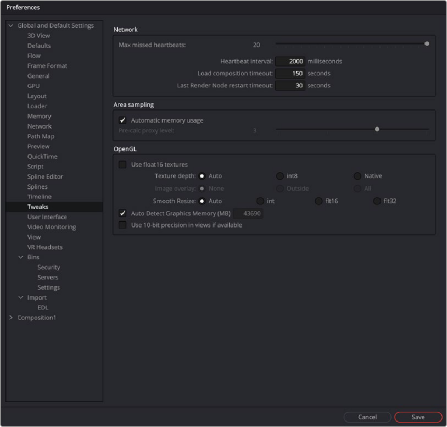
The Tweaks preferences
Network
The Network section is used to control and monitor the health of communication packets over TCP/IP when rendering over a network in Fusion Studio.
— Maximum Missed Heartbeats: This setting determines the maximum number of times the network is checked before terminating the communication with a Render node.
— Heartbeat Interval: This sets the time between network checks.
— Load Composition Timeout: This timeout option determines how long the Render Manger will wait for a composition to load before moving on to another task.
— Last Slave Restart Timeout: This timeout option determines how long the Render Manager will wait for a render salve to respond before using another render slave.
File I/O
The File I/O options are used to control the performance when reading frames or large media files from both direct and networked attached storage.
— I/O Canceling: This option enables a feature of the operating system that allows queued operations to be canceled when the function that requested them is stopped. This can improve the responsiveness, particularly when loading large images over a network.
Enabling this option will specifically affect performance while loading and accessing formats that perform a large amount of seeking, such as the TIFF format.
This option has not been tested with every hardware and OS configuration, so it is recommended to enable it only after you have thoroughly tested your hardware and OS configuration using drive loads from both local disks and network shares.
![]()
— Enable Direct Reads: Enabling this checkbox uses a more efficient method when loading a large chunk of contiguous data into memory by reducing I/O operations. Not every operating system employs this ability, so it may produce unknown behavior.
— Read Ahead Buffers: This slider determines the number of 64K buffers that are use to read ahead in a file I/O operation. The more buffers, the more efficient loading frames from disk will be, but the less responsive it will be to changes that require disk access interactively.
Area Sampling
The Area Sampling options allow you to fine-tune the RAM usage on Render nodes by trading off speed for lower RAM requirements.
— Automatic Memory Usage: This checkbox determines how area sampling uses available memory. Area sampling is used for Merges and Transforms. When the checkbox is enabled (default), Fusion will detect available RAM when processing the tool and determine the appropriate trade-off between speed and memory.
If less RAM is available, Fusion will use a higher proxy level internally and take longer to render. The quality of the image is not compromised in any way, just the amount of time it takes to render. In node trees that deal with images larger than 4K, it may be desirable to override the automatic scaling and fix the proxy scale manually. This can preserve RAM for future operations.
— Pre-Calc Proxy Level: Deselecting the Automatic Memory will enable the Pre-Calc Proxy Scale slider. Higher values will use less RAM but take much longer to render.
Open GL
This section controls how Fusion makes use of your graphics card when compositing in 3D with the Renderer 3D node. Most settings may be left as they are, but since OpenGL hardware varies widely in capabilities and different driver revisions can sometimes introduce bugs, these tweaks can be useful if you are experiencing unwanted behavior.
— Disable View LUT Shaders: OpenGL shaders can often dramatically accelerate View LUTs, but this can occasionally involve small trade-offs in accuracy. This setting will force Fusion to process LUTs at full accuracy using the CPU instead. Try activating this if View LUTs do not seem to be giving the desired result.
— Use Float16 Textures: If your graphics hardware supports 16-bit floating-point textures, activating this option will force int16 and float32 images to be uploaded to the viewer as float16 instead, which may improve playback performance.
— Texture Depth: Defines in what depth images are uploaded to the viewer.
— Auto: The Auto option (recommended) lets Fusion choose the best balance of performance and capability.
— int8: Similar to the Use Float16 Textures switch, this option can be used to force images to be uploaded to the Display View as int8, which can be faster but gives less range for View LUT correction.
— Native: The Native option uploads images at their native depth, so no conversion is done.
— Image Overlay: The Image Overlay is a viewer control used with Merge and Transform tools to display a translucent overlay of the transformed image. This can be helpful in visualizing the
transformation when it is outside the image bounds but may reduce performance when selecting the tool if cache memory is low. There are three settings to choose from: None, Outside, and All.
— None: This setting never displays the translucent overlay or controls, which can reduce the need for background renders, in some cases resulting in a speed up of the display.
![]()
— Outside: This will display only those areas of the control that are outside the bounds of the image, which can reduce visual confusion.
— All: Displays all overlays of all selected tools.
— Smooth Resize: This setting can disable the viewer’s Smooth Resize behavior when displaying floating-point images. Some older graphics cards are not capable of filtering floating-point textures or may be very slow. If Smooth Resize does not work well with float images, try setting this to flt16 or int.
— Auto Detect Graphics Memory (MB): Having Fusion open alongside other OpenGL programs like 3D animation software can lead to a shortage of graphics memory. In those cases, you can manually reduce the amount of memory Fusion is allowed to use on the card. Setting this too low or too high may cause performance or data loss.
— Use 10-10-10-2 Framebuffer: If your graphics hardware and monitor support 30-bit color (Nvidia Quadro/AMD Radeon Pro, and some Nvidia GeForce/AMD Radeon), this setting will render viewers with 10 bits per primary accuracy, instead of 8 bits. Banding is greatly reduced when displaying 3D renders or images deeper than 8-bit.